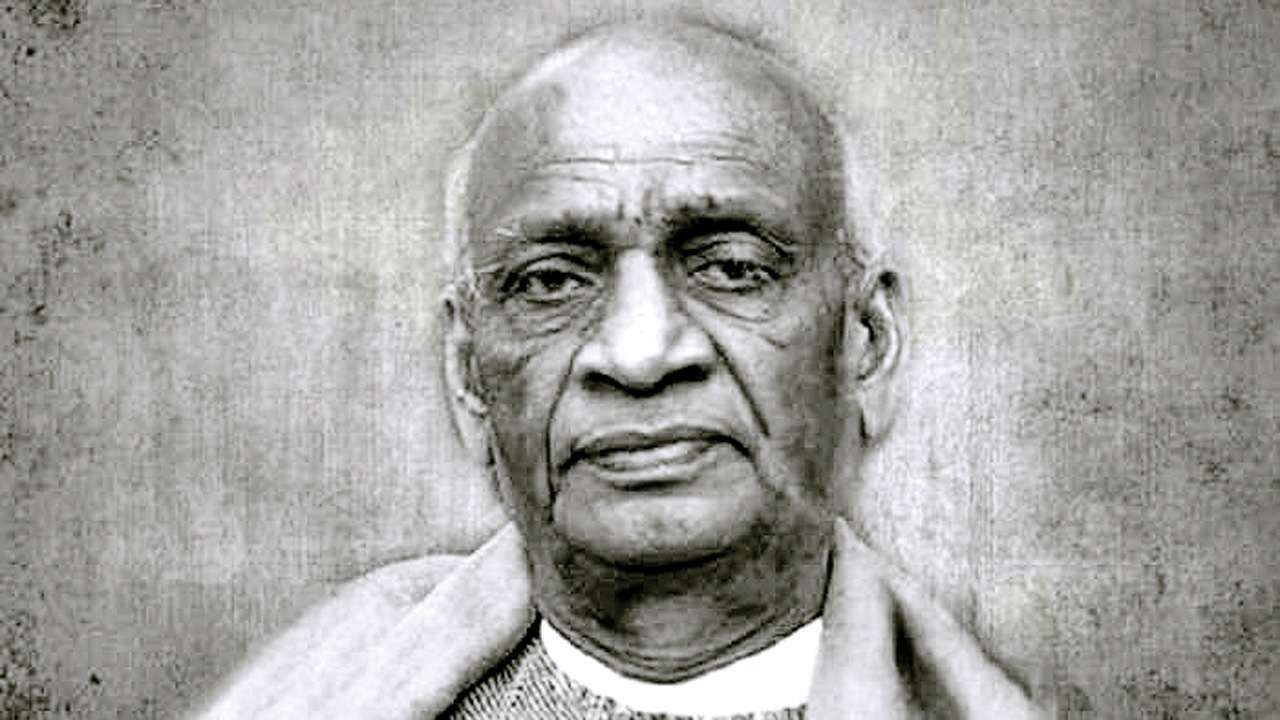
Vallabhbhai Patel (born October 31, 1875, Nadiad, Gujarat, India—died December 15, 1950, Bombay [now Mumbai]) Indian barrister and statesman, one of the leaders of the Indian National Congress during the struggle for Indian independence. During the first three years of Indian independence after 1947, he served as deputy prime minister, minister of home affairs, minister of information, and minister of states.
Early life and legal career
Patel was born into a self-sufficient landowning family of the Leva Patidar caste. Reared in an atmosphere of traditional Hinduism, he attended primary school at Karamasad and high school at Petlad but was mainly self-taught. Patel married at the age of 16, matriculated at 22, and passed the district pleader’s examination, which enabled him to practice law. In 1900 he set up an independent office of district pleader in Godhra, and two years later he moved to Borsad.
As a lawyer, Patel distinguished himself in presenting an unassailable case in a precise manner and in challenging police witnesses and British judges. In 1908 Patel lost his wife, who had borne him a son and daughter, and thereafter remained a widower. Determined to enhance his career in the legal profession, Patel traveled to London in August 1910 to study at the Middle Temple. There he studied diligently and passed the final examinations with high honours.
Returning to India in February 1913, he settled in Ahmadabad, rising rapidly to become the leading barrister in criminal law at the Ahmadabad bar. Reserved and courteous, he was noted for his superior mannerisms, his smart, English-style clothes, and his championship in bridge at Ahmadabad’s fashionable Gujarat Club. He was, until 1917, indifferent to Indian political activities.
In 1917 Patel found the course of his life changed after having been influenced by Mohandas K. Gandhi. Patel adhered to Gandhi’s satyagraha (policy of nonviolence) insofar as it furthered the Indian struggle against the British. But he did not identify himself with Gandhi’s moral convictions and ideals, and he regarded Gandhi’s emphasis on their universal application as irrelevant to India’s immediate political, economic, and social problems. Nevertheless, having resolved to follow and support Gandhi, Patel changed his style and appearance. He quit the Gujarat Club, dressed in the white cloth of the Indian peasant, and ate in the Indian manner.
From 1917 to 1924 Patel served as the first Indian municipal commissioner of Ahmadabad and was its elected municipal president from 1924 to 1928. Patel first made his mark in 1918, when he planned mass campaigns of peasants, farmers, and landowners of Kaira, Gujarat, against the decision of the Bombay government to collect the full annual revenue taxes despite crop failures caused by heavy rains.
In 1928 Patel successfully led the landowners of Bardoli in their resistance against increased taxes. His efficient leadership of the Bardoli campaign earned him the title sardar (“leader”), and henceforth he was acknowledged as a nationalist leader throughout India. He was considered practical, decisive, and even ruthless, and the British recognized him as a dangerous enemy.
Political philosophy
Patel, however, was no revolutionary. In the crucial debate over the objectives of the Indian National Congress during the years 1928 to 1931, Patel believed (like Gandhi and Motilal Nehru, but unlike Jawaharlal Nehru and Subhas Chandra Bose) that the goal of the Indian National Congress should be dominion status within the British Commonwealth—not independence. In contrast to Jawaharlal Nehru, who condoned violence in the struggle for independence, Patel ruled out armed revolution, not on moral but on practical grounds. Patel held that it would be abortive and would entail severe repression. Patel, like Gandhi, saw advantages in the future participation of a free India in a British Commonwealth, provided that India was admitted as an equal member. He emphasized the need to foster Indian self-reliance and self-confidence, but, unlike Gandhi, he did not regard Hindu-Muslim unity as a prerequisite for independence.
Patel disagreed with Jawaharlal Nehru on the need to bring about economic and social changes by coercion. A conservative rooted in traditional Hindu values, Patel belittled the usefulness of adapting socialist ideas to the Indian social and economic structure. He believed in free enterprise, thus gaining the trust of conservative elements, and thereby collected the funds that sustained the activities of the Indian National Congress.
Patel was the second candidate after Gandhi to the presidency of the 1929 Lahore session of the Indian National Congress. Gandhi shunned the presidency in an attempt to prevent the adoption of the resolution of independence and exerted pressure on Patel to withdraw, mainly owing to Patel’s uncompromising attitude toward the Muslims; Jawaharlal Nehru was elected. During the 1930 Salt Satyagraha (prayer and fasting movement), Patel served three months’ imprisonment. In March 1931 Patel presided over the Karachi session of the Indian National Congress. He was imprisoned in January 1932. Released in July 1934, he marshaled the organization of the Congress Party in the 1937 elections and was the main contender for the 1937–38 Congress presidency. Again, because of Gandhi’s pressure, Patel withdrew and Jawaharlal Nehru was elected. Along with other Congress leaders, Patel was imprisoned in October 1940, released in August 1941, and imprisoned once more from August 1942 until June 1945.
During the war Patel rejected as impractical Gandhi’s nonviolence in the face of the then-expected Japanese invasion of India. On the transfer of power, Patel differed with Gandhi in realizing that the partition of the subcontinent into Hindu India and Muslim Pakistan was inevitable, and he asserted that it was in India’s interests to part with Pakistan.
Patel was the leading candidate for the 1945–46 presidency of the Indian National Congress, but Gandhi once again intervened for the election of Nehru. Nehru, as president of the Congress, was invited by the British viceroy to form an interim government. Thus, in the normal course of events, Patel would have been the first prime minister of India. During the first three years of independence, Patel was deputy prime minister, minister of home affairs, minister of information, and minister of states; above all, his enduring fame rests on his achievement of the peaceful integration of the princely Indian states into the Indian Union and the political unification of India.
The government of India was not in favour of having independent states within the nation as it would hamper the security of the nation as a whole. The British ruled over the Princely states for a long time and forcibly grabbed the states. At the time of independence, the time of the British withdrawal, they left a choice between Pakistan and India. As there are approximately more than 565 princely states, it was quite tough to control all the states individually. At that time, in 1947 the freedom fighter of India, Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel, proposed favorable terms for the merger and went to the princely states that were not willing to join the union with army forces and agreed to join India.
Discussion:
Integration of Princely States:
The Indian states that are ruled by princes separately i.e. princely states are grabbed by the British forcefully into the provinces which constituted their “Empire of India”, this is the first policy of annexation. The second policy was the policy of indirect rule, here the British assumed “Paramountcy” on the princely states.
As per the Indian Independence Act of 1947, princely states are given an option. Those are either joined with the two newly born dominions India or Pakistan or continue as independent states. On that point, more of the 500 princely states already constituted 28% of its population with pre independent India and covered approx 48% area of the pre independent India. These princely states are not legally part of British India.The Travancore the Southern Indian maritime state was rich in “human and mineral resources”. In 1946, the Dewan, Sir C.P. Ramamswamy Aiyar of Travancore, decided to form an independent state as it has a huge resources of human and mineral and secretly had a relationship with the UK government. But in further days, due to some conflict, in 1947, on 30th of July, Travancore had joined with the India Union.
“Kashmir” was the princely state, where hindu king was ruling over the muslim population which means the state can join with any of India or Pakistan. The ruler of Kashmir, “Maharaja Hari Singh” was offered by both India and Pakistan a standstill agreement. In 1954, the president subsequently issued an order of constitution under“Article 370”. As per the “Section 3” the “Jammu & Kashmir” is a part of the Union of India. Within days, Hyderabad, Bhopal along with 565 states were merged with the Union of India.
Role of sardar patel in integration of princely states:
India’s first deputy prime minister and the home minister, Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel was given the formidable task with the secretary of the ministry of the states, V.P menon, to integrate the princely states. Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel kept trying to convince the princely states to join India. At that time, he also introduced a new concept that is “Privy Purses”. As per that concept, the royal families of the states will be provided a huge amount of payment through an agreement to merge with India. Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel took many positive steps to merge the princely states with the Union of India.
States such as Bikaner, Baroda and few more states of Rajasthan decided to join the Union and they are the first ones. On the other hand, there were several more states who wanted to join with Pakistan and some other states wanted to live as independent states. This way some princely states become part of Pakistan.
The “Rajput” princely state i.e. “Jodhpur ”, had a Hindu king and a large Hindu population. But the strange thing is, the state is leaning towards Pakistan. The Jinnah of Pakistan gifted the prince of Jodhpur, “Hanvant Singh”, a signed blank check. He also offered him access to the “Karachi Port”. Seeing that, the Iron Man of India, Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel immediately offered a sufficient amount with sufficient benefits to the king of “Jodhpur”- “Hanvant Singh”. Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel gave the most effort to merge the “Jodhpur” state with India. As the “Kathiawar rail” is connected with “Jodhpur” and India would supply different grains at the time of famines through that way, Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel did not want to lose the state.
Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel worked effortlessly to integrate the princely states with the Union of India that gave the country huge assets as most countries hold a huge amount of wealth. Along with that many of the states were involved with many of the vital works such as trending, import, export of India.